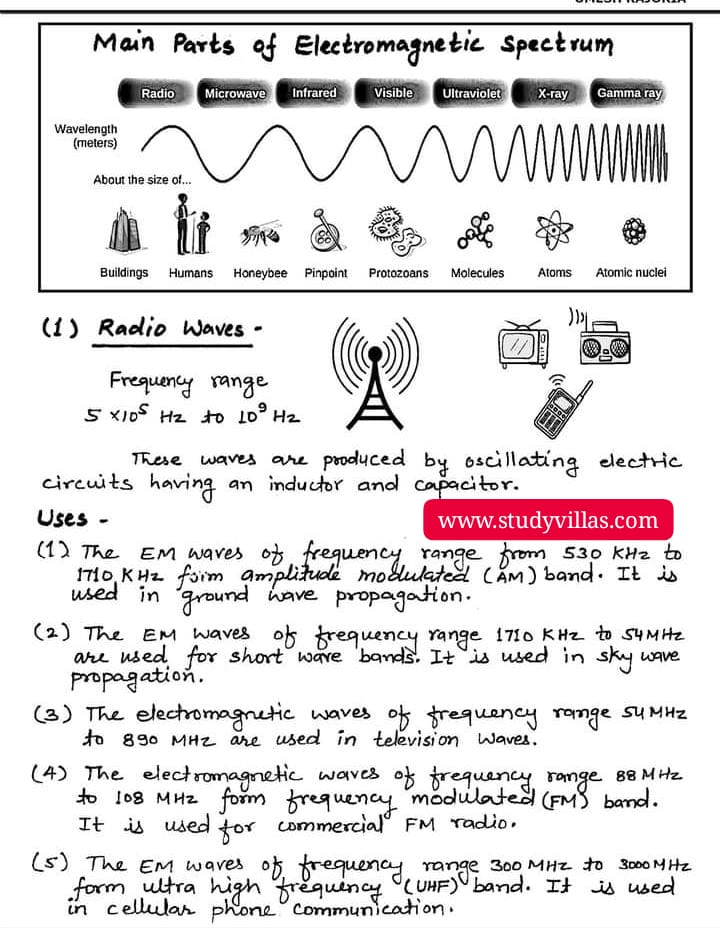
Electromagnetic Spectrum And main parts of electromagnetic spectrum physics handwritten notes
Defination:
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation, including:
– Radio waves
– Microwaves
– Infrared (IR) radiation
– Visible light
– Ultraviolet (UV) radiation
– X-rays
– Gamma rays
It is a continuous spectrum, meaning that there are no gaps or boundaries between the different types of radiation. Instead, they blend smoothly into one another, with each type of radiation having a shorter wavelength and higher frequency than the one before it.
The electromagnetic spectrum is often depicted as a linear diagram, with wavelength on one axis and frequency on the other. This diagram shows how the different types of radiation are related and how they vary in terms of their properties and uses.
Here’s a simple definition:
Electromagnetic Spectrum: The entire range of electromagnetic radiation, from low-frequency, long-wavelength radio waves to high-frequency, short-wavelength gamma rays.
The electromagnetic spectrum is a vast range of frequencies, including:
1. Radio waves: Longest wavelength, lowest frequency (e.g., FM radio, AM radio)
2. Microwaves: Used for heating, cooking, and wireless communication (e.g., microwave ovens, cell phones)
3. Infrared (IR) radiation: Heat, thermal imaging, and remote sensing (e.g., thermal cameras, night vision)
4. Visible light: What we can see with our eyes (e.g., sunlight, light bulbs)
5. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation: Causes chemical reactions, used in disinfection and curing (e.g., UV lamps, sunlight)
6. X-rays: High-energy radiation for medical imaging and materials analysis (e.g., medical X-rays, airport security)
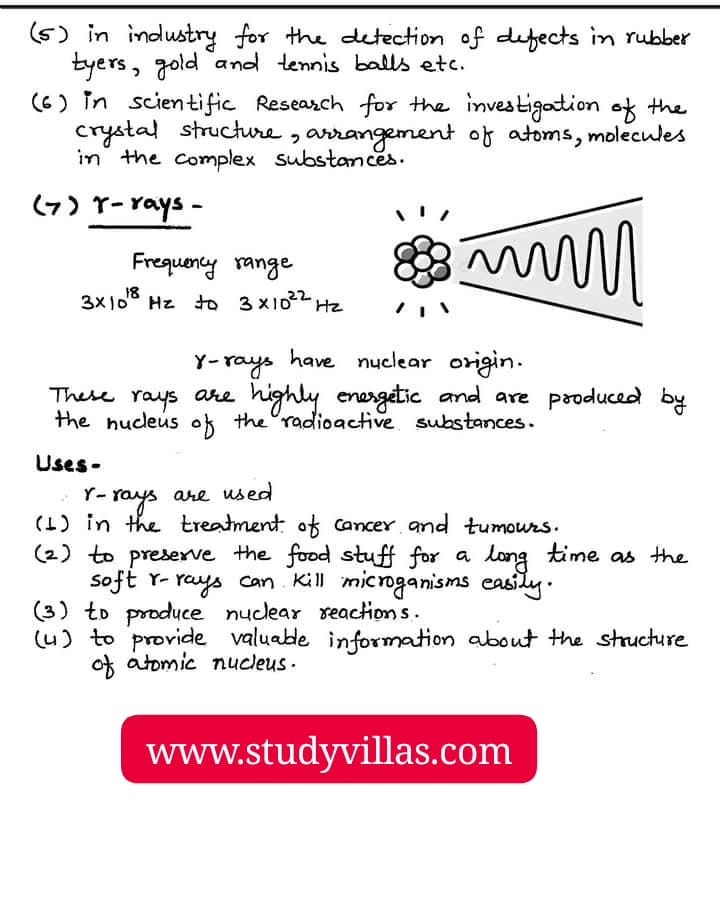
7. Gamma rays: Highest energy, used in medical treatment, sterilization, and scientific research (e.g., cancer treatment, food irradiation)
Each part of the spectrum has unique properties, uses, and effects on matter.
Here’s a rough ordering of the spectrum by wavelength and frequency:
– Radio waves: 1 mm – 10 km, 3 kHz – 300 GHz
– Microwaves: 1 mm – 1 m, 300 MHz – 300 GHz
– Infrared: 700 nm – 1 mm, 300 GHz – 400 THz
– Visible light: 400 nm – 700 nm, 400 THz – 800 THz
– Ultraviolet: 100 nm – 400 nm, 800 THz – 30 PHz
– X-rays: 0.01 nm – 10 nm, 30 PHz – 30 EHz
– Gamma rays: <0.01 nm, >30 EHz